Tutorial - Subscribe to ZED topics with NITROS in an Isaac™ ROS node
This tutorial demonstrates how to subscribe to ZED topics using NITROS in an Isaac™ ROS node. It assumes you have already set up the ZED camera and are publishing its data using the zed-ros2-wrapper packages as described in the Setting up Isaac™ ROS to work with ZED Cameras in ROS 2 section.
The example explains how to create a ROS 2 component that subscribes to the ZED camera’s image and depth streams, using NITROS and performs benchmarking on the received data. The same component also subscribes to ZED camera’s image and depth streams using standard ROS 2 subscriptions and performs benchmarking on the same received data for comparison.
Setup the example #
If you haven’t done so already, set up your development environment by following our NVIDIA® Isaac™ ROS installation guide.
Install the ZED ROS2 Examples packages in the workspace:
cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src && \
git clone https://github.com/stereolabs/zed-ros2-examples.git
If you are using Docker, start the Isaac™ ROS environment with ZED support:
cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src/isaac_ros_common && \
./scripts/run_dev.sh -i ros2_humble.zed \
-a "-v /usr/local/zed/settings:/usr/local/zed/settings \
-v /usr/local/zed/resources:/usr/local/zed/resources"
Build the Subscriber example application:
cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}
colcon build --symlink-install --packages-above zed_isaac_ros_nitros_sub
Create a ROS 2 Node with NITROS Subscriptions #
The ROS 2 node is implemented in C++ as a ROS 2 component. The source code is located in the folder isaac_ros/zed_isaac_ros_nitros_sub/src/component.
The component is defined as a class ZedNitrosSubComponentthat inherits from rclcpp::Node.
The Nitros subscriber is declared as a member variable of the class in the file include/zed_nitros_sub_component.hpp:
// Nitros subscriber to the image topic
std::shared_ptr<nvidia::isaac_ros::nitros::ManagedNitrosSubscriber<nvidia::isaac_ros::nitros::NitrosImageView>> _nitrosSub;
the Nitros subscriber is then initialized in the function create_nitros_subscriber() of the class in the file src/zed_nitros_sub_component.cpp:
void ZedNitrosSubComponent::create_nitros_subscriber()
{
// Create a Nitros subscriber to the Nitros topic
_nitrosSub = std::make_shared<nvidia::isaac_ros::nitros::ManagedNitrosSubscriber<
nvidia::isaac_ros::nitros::NitrosImageView>>(
this, "image",
_isDepth ? nvidia::isaac_ros::nitros::nitros_image_32FC1_t::supported_type_name :
nvidia::isaac_ros::nitros::nitros_image_rgba8_t::supported_type_name,
std::bind(
&ZedNitrosSubComponent::nitros_sub_callback, this,
std::placeholders::_1));
}
When creating the Nitros subscriber, we specify the topic name to subscribe to (image), and we must also specify the Nitros type of the topic.
The Nitros type must be one of the supported Nitros types of the ManagedNitrosSubscriber class. In this case, we are subscribing to either the image or depth topic of the ZED camera, which are of type sensor_msgs/msg/Image. The corresponding Nitros types are nitros_image_rgba8_t for the image topic and nitros_image_32FC1_t for the depth topic.
📌 Note: The Nitros type must be specified as a string, using the static member
supported_type_nameof the corresponding Nitros type class. It’s not possible to determine the Nitros type at runtime, so you must choose the correct type when creating the subscriber.
In the node we use a trick to determine at runtime whether we are subscribing to the image or depth topic. We use a parameter _isDepth that can be set by subscribing to the same topic using a standard ROS 2 subscription. When we receive the first message on the standard ROS 2 subscription, we check the encoding of the message to determine whether it’s an image or depth topic, and set the _isDepth parameter accordingly. This way, we can create the Nitros subscriber with the correct type:
static bool first_frame = true;
if (first_frame) {
_encoding = img->encoding;
first_frame = false;
if (img->encoding == "32FC1") {
_isDepth = true;
RCLCPP_DEBUG(this->get_logger(), "Receiving Depth map messages.");
} else if (img->encoding == "bgra8") {
_isDepth = false;
RCLCPP_DEBUG(this->get_logger(), "Receiving RGB image messages.");
} else {
RCLCPP_ERROR(
this->get_logger(),
"Received an unsupported image encoding: %s. Only BGRA and 32FC1 are supported.",
img->encoding.c_str());
rclcpp::shutdown();
}
}
The Nitros subscriber uses a callback function nitros_sub_callback() that is called whenever a new message is received on the subscribed topic. The callback function receives a NitrosImageView object that contains the image data and metadata:
void ZedNitrosSubComponent::nitros_sub_callback(
const nvidia::isaac_ros::nitros::NitrosImageView & img)
{
[...]
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "Receiving CUDA buffer with memory at: %p", img.GetGpuData());
RCLCPP_INFO(
this->get_logger(),
" * encoding: %s", img.GetEncoding().c_str());
RCLCPP_INFO(
this->get_logger(),
" * width: %d, height: %d",
img.GetWidth(), img.GetHeight());
[...]
}
How the example works #
The example node subscribes to the ZED camera’s image or depth topics using both NITROS and standard ROS 2 subscriptions. It performs benchmarking on the received data to compare the performance of NITROS and standard ROS 2 subscriptions.
At the start of the node, we create a standard ROS 2 subscription to the image topic and receive a number of messages as set by the parameter benchmark.tot_samples. We then perform benchmarking on the received messages to measure:
- The average latency of the messages with minimum and maximum latency and standard deviation.
- The average frame rate of the messages with minimum and maximum frame rate and standard deviation.
- The average CPU usage of the node performing the subscription process with minimum and maximum CPU usage and standard deviation.
- The average GPU usage of the node performing the subscription process with minimum and maximum GPU usage and standard deviation.
When the benchmarking is complete, we unsubscribe from the standard ROS 2 subscription and create the NITROS subscriber to the same topic and repeat the benchmarking process.
Finally, when we received benchmark.tot_samples messages with the NITROS subscriber, we print the benchmarking results, and compare the performance of NITROS and standard ROS 2 subscriptions.
The results of the benchmarking are printed to the console and saved to a CSV file defined by the parameter benchmark.csv_log_file.
Advanced configuration of the example #
The folder config contains a YAML file named example_params.yaml that defines the parameters of the example.
The section general is used to overwrite the setup of the ZED ROS2 Wrapper node:
grab_resolution: The native camera grab resolution. ‘HD1200’, ‘HD2K’, ‘HD1080’, ‘HD720’, ‘SVGA’, ‘VGA’, ‘AUTO’.grab_frame_rate: ZED SDK internal grabbing rate (FPS).pub_resolution: The resolution used for image and depth map publishing. ‘NATIVE’ to use the samegeneral.grab_resolution-CUSTOMto apply thegeneral.pub_downscale_factordownscale factory to reduce bandwidth in transmission.pub_downscale_factor: Rescale factor used to rescale image before publishing when ‘pub_resolution’ is ‘CUSTOM’rescale factor used to rescale image before publishing when ‘pub_resolution’ is ‘CUSTOM’.pub_frame_rate: Frequency of publishing of visual images and depth data. This value must be equal or less than the camera framerate (grab_frame_rate).
The section benchmark is used to configure the benchmarking process:
tot_samples: Total number of samples to process.cpu_gpu_load_period: Period in milliseconds to retrieve CPU and GPU load statistics.cpu_gpu_load_avg_wnd_size: Number of samples to use to compute the average CPU and GPU load average.csv_log_file: If not empty, log the benchmark results in a CSV file with the specified name.
The section debug is used to debug the nodes:
debug_nitros: Enable Nitros debug information.use_pub_timestamps: Used to measure the real communication latency. If true, the latency is measured by setting the timestamps in the header of the messages to the system time just before publishing. If false, the latency is measured using the ZED camera timestamps, when the data is grabbed from the camera. This method allows to retrieve the end-to-end latency, the full time it takes for a message to travel from the camera buffer to the subscriber.
Run the example #
First, make sure you compiled and built the example as described in the Setup section.
📌 Note: If you are using Docker, make sure to start the Isaac™ ROS environment with ZED support:
cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src/isaac_ros_common && \ ./scripts/run_dev.sh -i ros2_humble.zed \ -a "-v /usr/local/zed/settings:/usr/local/zed/settings \ -v /usr/local/zed/resources:/usr/local/zed/resources"
To launch the example, you must first select the topic to subscribe to. The launch file requires you to specify the topic name using the argument topic_name. For example, to subscribe to the image topic, use topic_name:=/zed_isaac/zed/rgb/rect/image, or to subscribe to the depth topic, use topic_name:=/zed_isaac/zed/depth/depth_registered.
ros2 launch zed_isaac_ros_subscriber zed_isaac_ros_subscriber.launch.py \
camera_model:=<camera_model> \
topic_name:=<topic_name>
for example, to subscribe to the RGB image topic of a ZED X One GS camera:
ros2 launch zed_isaac_ros_nitros_sub zed_nitros_sub_example.launch.py \
camera_model:=zedxonegs \
topic_name:=/zed_isaac/zed/rgb/rect/image
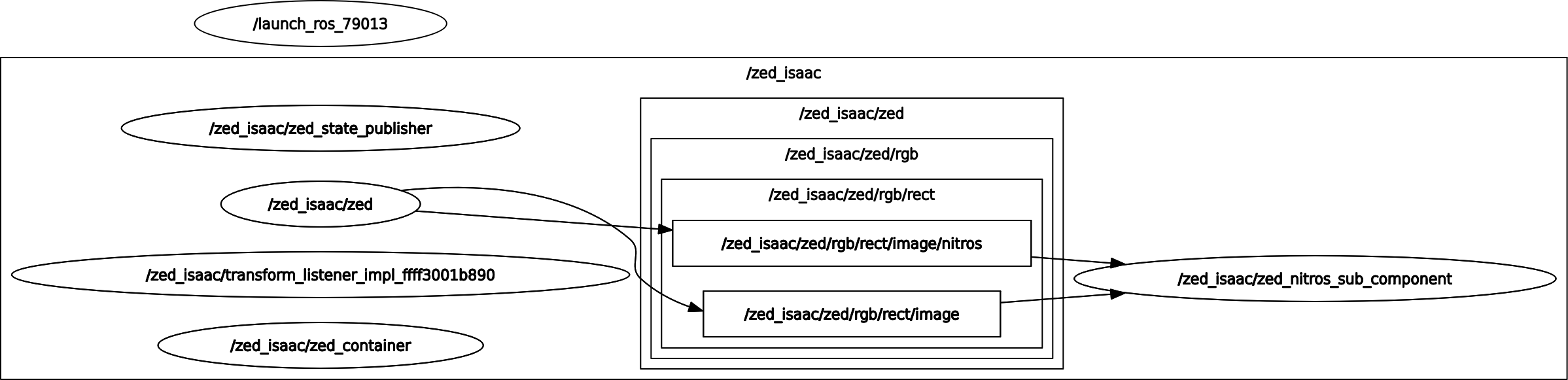
📌 Note: If you list all the topics published by the ZED ROS2 Wrapper node using the command
ros2 topic list, you will see that all the image and depth topics have also a suffix/nitros. You do not need to specify that suffix when subscribing to the topics using NITROS, as the Managed NITROS subscriber automatically subscribes to the Nitros topic when possible. You can confirm this by looking at the ROS 2 Node Graph using the commandros2 run rqt_graph rqt_graph.
Example output #
The example will print the benchmarking results to the console when the benchmarking is complete.
We executed the example on an NVIDIA® Jetson AGX Orin, using a ZED X One GS camera running at HD1200 @ 60 FPS.
The console output will look something like this:
[...]
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744150580] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: +++ Logging benchmark results in CSV file: zed_nitros_benchmark.csv +++
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744330579] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: -----------------------------------
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744351379] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: DDS Subscriber benchmark results:
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744370067] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: - DDS Subscriber Frequency:
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744381203] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Samples: 999
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744390514] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Min: 44.174638 Hz
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744408242] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Max: 142.249595 Hz
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744418514] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Avg: 60.175589 Hz
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744427730] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Std Dev: 5.622423 Hz
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744541681] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: - DDS Subscriber Latency:
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744561329] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Samples: 1000
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744572689] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Min: 0.003968 sec
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744583761] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Max: 0.009541 sec
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744592561] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Avg: 0.004779 sec
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744600753] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Std Dev: 0.000628 sec
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744639249] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: - DDS Subscriber CPU Load:
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744651888] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Samples: 1000
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744660272] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Min: 17.606060 %
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744669552] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Max: 41.618382 %
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744678352] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Avg: 27.433345 %
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744686512] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Std Dev: 3.704680 %
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744721808] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: - DDS Subscriber GPU Load:
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744734416] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Samples: 1000
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744742416] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Min: 21.520000 %
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744751632] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Max: 54.620003 %
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744760368] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Avg: 38.697240 %
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744801103] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Std Dev: 5.602721 %
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744835983] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: -----------------------------------
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744849231] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: Nitros Subscriber benchmark results:
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744860879] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: - Nitros Subscriber Frequency:
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744868175] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Samples: 999
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744875503] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Min: 50.950175 Hz
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744884751] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Max: 72.570341 Hz
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744893039] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Avg: 59.790936 Hz
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744901231] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Std Dev: 2.425483 Hz
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744935406] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: - Nitros Subscriber Latency:
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744947246] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Samples: 1000
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744955438] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Min: 0.000217 sec
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744963822] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Max: 0.001925 sec
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744971950] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Avg: 0.000405 sec
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.744982574] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Std Dev: 0.000113 sec
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.745013870] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: - Nitros Subscriber CPU Load:
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.745027054] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Samples: 1000
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.745035278] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Min: 13.585081 %
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.745044974] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Max: 38.929817 %
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.745053005] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Avg: 24.584492 %
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.745061197] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Std Dev: 3.663143 %
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.745092013] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: - Nitros Subscriber GPU Load:
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.745103757] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Samples: 1000
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.745111437] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Min: 20.240000 %
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.745120397] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Max: 52.659996 %
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.745128941] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Avg: 37.184940 %
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.745137101] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Std Dev: 5.907662 %
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.745165741] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: -----------------------------------
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.745177325] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: Benchmark comparison:
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.745213932] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]:
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.745240268] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * DDS Subscriber Latency vs Nitros Subscriber Latency
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.745261644] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Avg: 0.00477946 sec vs 0.000404906 sec
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.745284172] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: - DDS Subscriber Latency is higher by 0.00437456 sec (1080.39%)
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.745320267] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]:
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.745339243] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * DDS Subscriber Frequency vs Nitros Subscriber Frequency
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.745358443] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Avg: 60.1756 Hz vs 59.7909 Hz
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.745378571] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: - DDS Subscriber Frequency is higher by 0.384653 Hz (0.64333%)
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.745413771] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]:
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.745432107] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * DDS Subscriber CPU Load vs Nitros Subscriber CPU Load
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.745450410] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Avg: 27.4333 % vs 24.5845 %
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.745468778] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: - DDS Subscriber CPU Load is higher by 2.84885 % (11.588%)
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.745501386] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]:
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.745546122] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * DDS Subscriber GPU Load vs Nitros Subscriber GPU Load
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.745568298] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: * Avg: 38.6972 % vs 37.1849 %
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.745588073] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: - DDS Subscriber GPU Load is higher by 1.5123 % (4.06697%)
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.745608681] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: -----------------------------------
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.745620265] [zed_isaac.zed_nitros_sub_component]: Shutting down the node...
[component_container_mt-1] [INFO] [1759761477.867231955] [zed_isaac.zed]: === CLOSING CAMERA ===
If you specified a CSV log file in the parameters, the benchmarking results will be saved to the specified file. If you set it as a filename, without the path, the file will be saved in the ISAAC_ROS_WS directory.
This is an example of the contents of the CSV log file:
BENCHMARK, SAMPLES, UNITS, AVG, MIN, MAX, STDDEV
DDS Subscriber Frequency, 999, Hz, 60.1756, 44.1746, 142.25, 5.62242
DDS Subscriber Latency, 1000, sec, 0.00477946, 0.00396776, 0.00954056, 0.000627538
DDS Subscriber CPU Load, 1000, %, 27.4333, 17.6061, 41.6184, 3.70468
DDS Subscriber GPU Load, 1000, %, 38.6972, 21.52, 54.62, 5.60272
Nitros Subscriber Frequency, 999, Hz, 59.7909, 50.9502, 72.5703, 2.42548
Nitros Subscriber Latency, 1000, sec, 0.000404906, 0.000216722, 0.00192523, 0.000112669
Nitros Subscriber CPU Load, 1000, %, 24.5845, 13.5851, 38.9298, 3.66314
Nitros Subscriber GPU Load, 1000, %, 37.1849, 20.24, 52.66, 5.90766
* DDS Subscriber Latency vs Nitros Subscriber Latency
* Avg: 0.00477946 sec vs 0.000404906 sec
- DDS Subscriber Latency is higher by 0.00437456 sec (1080.39%)
* DDS Subscriber Frequency vs Nitros Subscriber Frequency
* Avg: 60.1756 Hz vs 59.7909 Hz
- DDS Subscriber Frequency is higher by 0.384653 Hz (0.64333%)
* DDS Subscriber CPU Load vs Nitros Subscriber CPU Load
* Avg: 27.4333 % vs 24.5845 %
- DDS Subscriber CPU Load is higher by 2.84885 % (11.588%)
* DDS Subscriber GPU Load vs Nitros Subscriber GPU Load
* Avg: 38.6972 % vs 37.1849 %
- DDS Subscriber GPU Load is higher by 1.5123 % (4.06697%)
The output shows the benchmarking results for both the DDS subscriber and the Nitros subscriber, including the average, minimum, maximum, and standard deviation for each metric. It also includes a comparison of the two subscribers for each metric.
For example, in the output above, we can see that the average latency of the DDS subscriber is 0.00477946 sec, while the average latency of the Nitros subscriber is 0.000404906 sec. This means that the Nitros subscriber has a significantly lower latency than the DDS subscriber, 1080.39% lower in this case.
While the frame rate of the DDS subscriber is slightly higher than that of the Nitros subscriber, the difference is minimal (0.64333% higher for DDS), the standard deviation is also higher for the DDS subscriber, indicating that the frame rate is more stable with the Nitros subscriber.
The launch file explained #
The launch file is located in the folder launch and is named zed_isaac_ros_nitros_sub.launch.py.
The launch file is responsible for starting all the necessary nodes and configurations for example. It sets up the parameters, including the ZED camera settings and the benchmarking parameters, and launches the required nodes in a ROS 2 component container.
Retrieve the path to the configuration file:
example_params_file = os.path.join(
get_package_share_directory('zed_isaac_ros_nitros_sub'),
'config',
'example_params.yaml'
)
Set the namespace and define the launch arguments:
namespace_val = 'zed_isaac'
camera_model = LaunchConfiguration('camera_model')
topic_name = LaunchConfiguration('topic_name')
Create the ROS 2 component container to run the nodes:
container_name = 'zed_container'
info = '* Starting Composable node container: ' + namespace_val + '/' + container_name
actions.append(LogInfo(msg=TextSubstitution(text=info)))
# Note: It is crucial that the 'executable' field is set to be 'component_container_mt'
# so that the created nodes can be started and communicated correctly within the same process.
zed_container = ComposableNodeContainer(
name=container_name,
namespace=namespace_val,
package='rclcpp_components',
executable='component_container_mt',
arguments=['--ros-args', '--log-level', 'info'],
output='screen',
)
actions.append(zed_container)
Call the ZED ROS2 Wrapper launch file to start the ZED camera node, passing the necessary arguments, including the camera model, namespace, and parameters file:
# ZED Wrapper launch file
zed_wrapper_launch = IncludeLaunchDescription(
launch_description_source=PythonLaunchDescriptionSource([
get_package_share_directory('zed_wrapper'),
'/launch/zed_camera.launch.py'
]),
launch_arguments={
'camera_model': camera_model,
'container_name': container_name,
'namespace': namespace_val,
'enable_ipc': 'false',
'ros_params_override_path': example_params_file
}.items()
)
actions.append(zed_wrapper_launch)
📌 Note: The
enable_ipcargument is set tofalsebecause the Nitros subscriber does not support IPC transport.** This is a mandatory setting when using NITROS**.
Add the ZED Isaac NITROS Subscriber component to the container, passing the necessary arguments, and remapping the topic name to subscribe to:
isaac_image_sub_node = ComposableNode(
package='zed_isaac_ros_nitros_sub',
plugin='stereolabs::ZedNitrosSubComponent',
name='zed_nitros_sub_component',
namespace=namespace_val,
remappings=[
('image', topic_name)
],
parameters=[
example_params_file
],
extra_arguments=[{'use_intra_process_comms': False}]
)
📌 Note: Again, the
use_intra_process_commsargument is set toFalsebecause the Nitros subscriber does not support intra-process communication. This is a mandatory setting when using NITROS.
Finally, load the subscriber component into the container:
container_full_name = namespace_val + '/' + container_name
# Load the Image Subscriber node into the container
load_sub_node = LoadComposableNodes(
composable_node_descriptions=[isaac_image_sub_node],
target_container=container_full_name
)
actions.append(load_sub_node)
Conclusion #
This tutorial demonstrated how to subscribe to ZED camera topics using NITROS in an Isaac™ ROS node. We created a ROS 2 component that subscribes to the ZED camera’s image and depth streams using both NITROS and standard ROS 2 subscriptions, and performed benchmarking on the received data to compare the performance of the two methods.
The results showed that the NITROS subscriber has significantly lower latency compared to the standard ROS 2 subscription, while maintaining a comparable frame rate. Additionally, the CPU and GPU usage were also lower for the NITROS subscriber, indicating better efficiency.
The values of the standard deviation for the Nitros subscriber are also lower, indicating a more stable performance.
This example can be used as a starting point for integrating ZED cameras into your Isaac™ ROS applications, leveraging the performance benefits of NITROS for high-throughput data streams.
