Tutorial - AprilTag Detection with ZED and Isaac™ ROS
This tutorial demonstrates how to create an Isaac™ ROS application using AprilTag detection as example. It assumes you have already set up the ZED camera and are publishing its data using the zed-ros2-wrapper packages as described in the Setting up Isaac™ ROS to work with ZED Cameras in ROS 2 section.
The application will subscribe to the ZED camera’s image stream, convert the ZED images to a supported format, and finally process the images to detect AprilTags, and publish the detected tags’ information.
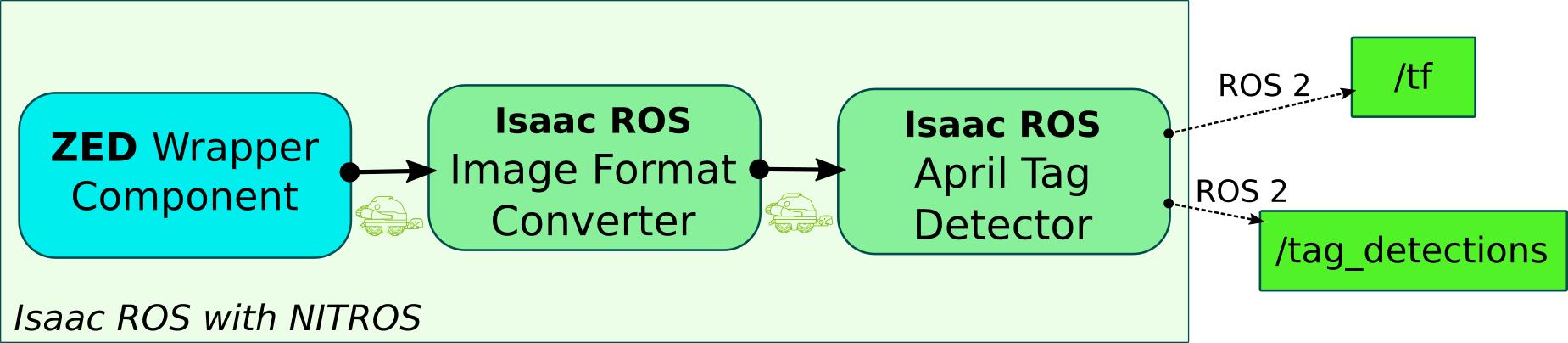
The example leverages the NITROS communication framework for efficient data exchange between the ZED camera and the AprilTag detection module through the GPU memory without unnecessary data copies on CPU.
📌 Note: It is not required to rectify the images for AprilTag detection, because the ZED Wrapper component handles any necessary image preprocessing in the GPU memory through the ZED SDK.
Please refer to the official NVIDIA® documentation for more details on the Image Format Converter and AprilTag Isaac™ ROS nodes.
Setup the example #
If you haven’t done so already, set up your development environment by following our NVIDIA® Isaac™ ROS installation guide.
Install the ZED ROS2 Examples packages in the workspace:
cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src && \
git clone https://github.com/stereolabs/zed-ros2-examples.git
If you are using Docker, start the Isaac™ ROS environment with ZED support:
cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src/isaac_ros_common && \
./scripts/run_dev.sh -i ros2_humble.zed \
-a "-v /usr/local/zed/settings:/usr/local/zed/settings \
-v /usr/local/zed/resources:/usr/local/zed/resources"
Install the Isaac™ ROS AprilTag and Image Process packages in the workspace:
sudo apt-get update && \
sudo apt-get install -y ros-humble-isaac-ros-apriltag ros-humble-isaac-ros-image-proc
Build the AprilTag detection application:
cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS} && \
colcon build --symlink-install --packages-above zed_isaac_ros_april_tag
Run the AprilTag detection application #
Before running the AprilTag detection application you must configure the example.
cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src/zed-ros2-examples/isaac_ros/zed_isaac_ros_april_tag/config
Modify the zed_isaac_ros_april_tag.yaml file to configure the AprilTag detection parameters:
/**:
ros__parameters:
size: 0.155
max_tags: 64
tile_size: 4
tag_family: 'tag36h11' # Tag family to detect. CUDA backend only supports tag36h11. CPU and PVA backends support tag36h11, tag16h5, tag25h9, tag36h10, tag36h11, circle21h7, circle49h12, custom48h12, standard41h12, standard52h13
backends: 'CUDA' # Backend to perform detection with. Options include CPU, CUDA, PVA
size: The size of the AprilTag in meters (e.g., 0.155).max_tags: The maximum number of tags to detect (e.g., 64).tile_size: The tile/window size for adaptive thresholding in pixels (e.g., 4).tag_family: The family of AprilTags to detect. CUDA backend only supportstag36h11. CPU and PVA backends supporttag36h11,tag16h5,tag25h9,tag36h10,tag36h11,circle21h7,circle49h12,custom48h12,standard41h12,standard52h13backends: The backend to use for detection. Options includeCPU,CUDA,PVA.
You can generate the April Tags using the tool at this page.
Modify the zed_params.yaml file to configure the ZED camera parameters:
/**:
ros__parameters:
general:
grab_resolution: 'HD1080'
grab_frame_rate: 30
pub_resolution: 'CUSTOM'
pub_downscale_factor: 2.0
pub_frame_rate: 30.0
grab_resolution: The native camera grab resolution. Options includeHD2K,HD1200,HD1080,HD720,SVGA,AUTO.grab_frame_rate: The ZED SDK internal grabbing rate. Options include60,30,15forHD1200/HD1080and120,60,30,15forSVGA.pub_resolution: The resolution used for image and depth map publishing. Options includeNATIVEandCUSTOM. SetNATIVEto use the samegeneral.grab_resolution; setCUSTOMto apply thegeneral.pub_downscale_factordownscale factory to reduce bandwidth in data transmission.pub_downscale_factor: The rescale factor used to rescale the image before publishing whenpub_resolutionisCUSTOM.pub_frame_rate: The data publishing frame rate.
Visualize Results #
First, make sure you compiled and built the example as described in the Setup section.
📌 Note: If you are using Docker, make sure to start the Isaac™ ROS environment with ZED support:
cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src/isaac_ros_common && \ ./scripts/run_dev.sh -i ros2_humble.zed \ -a "-v /usr/local/zed/settings:/usr/local/zed/settings \ -v /usr/local/zed/resources:/usr/local/zed/resources"
Start the processing by using the command:
ros2 launch zed_isaac_ros_april_tag zed_isaac_ros_april_tag.launch.py camera_model:=<camera_model>
where <camera_model> is the model of the ZED camera you are using (e.g., zedx, zed2i, etc.).
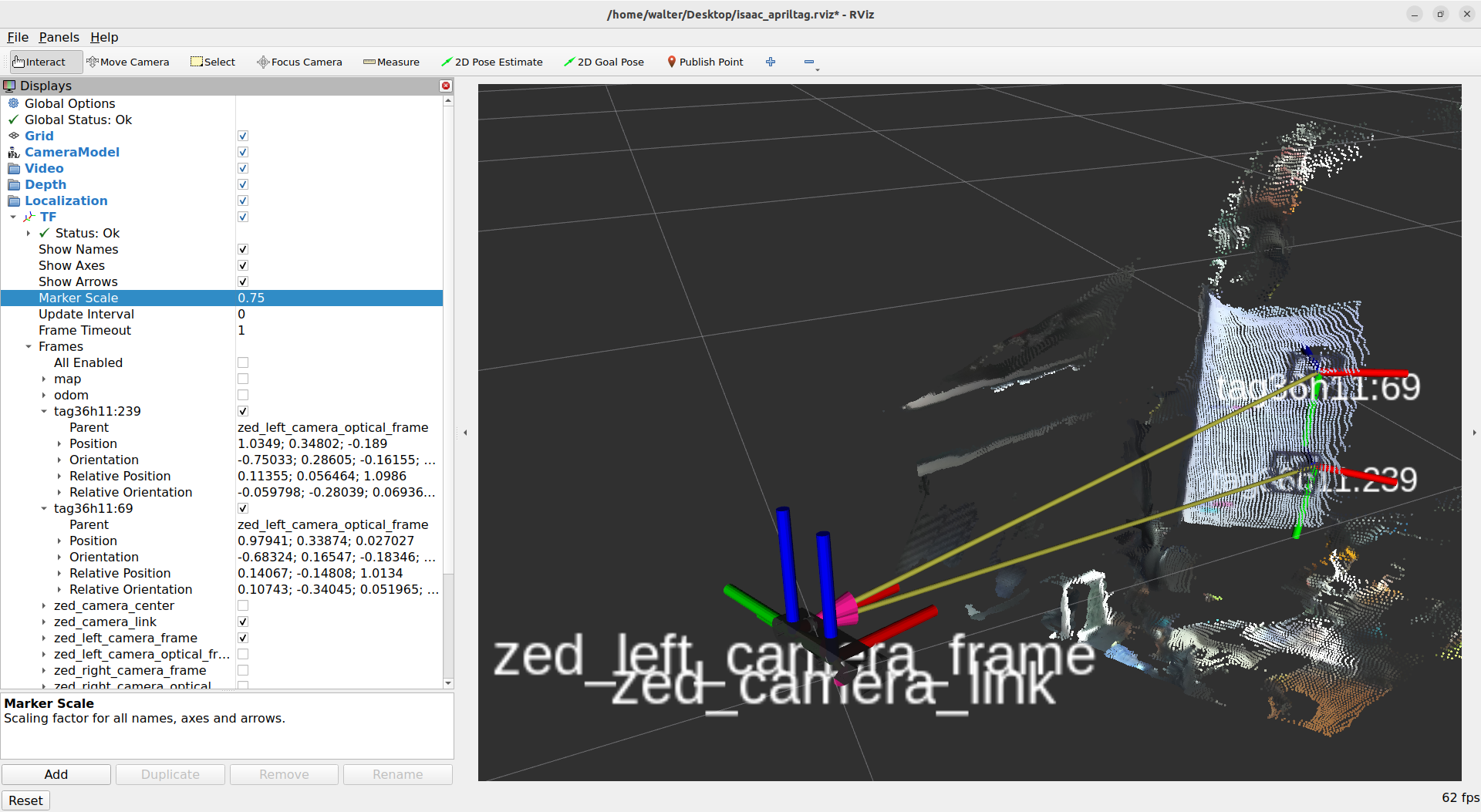
Point the camera to an AprilTag target and observe the AprilTag detection output /tag_detections on a separate terminal with the command:
ros2 topic echo /tag_detections
📌 Note: The AprilTag detection does not use the ZED depth information, so you can use this tutorial indifferently with a ZED stereo or monocular camera.
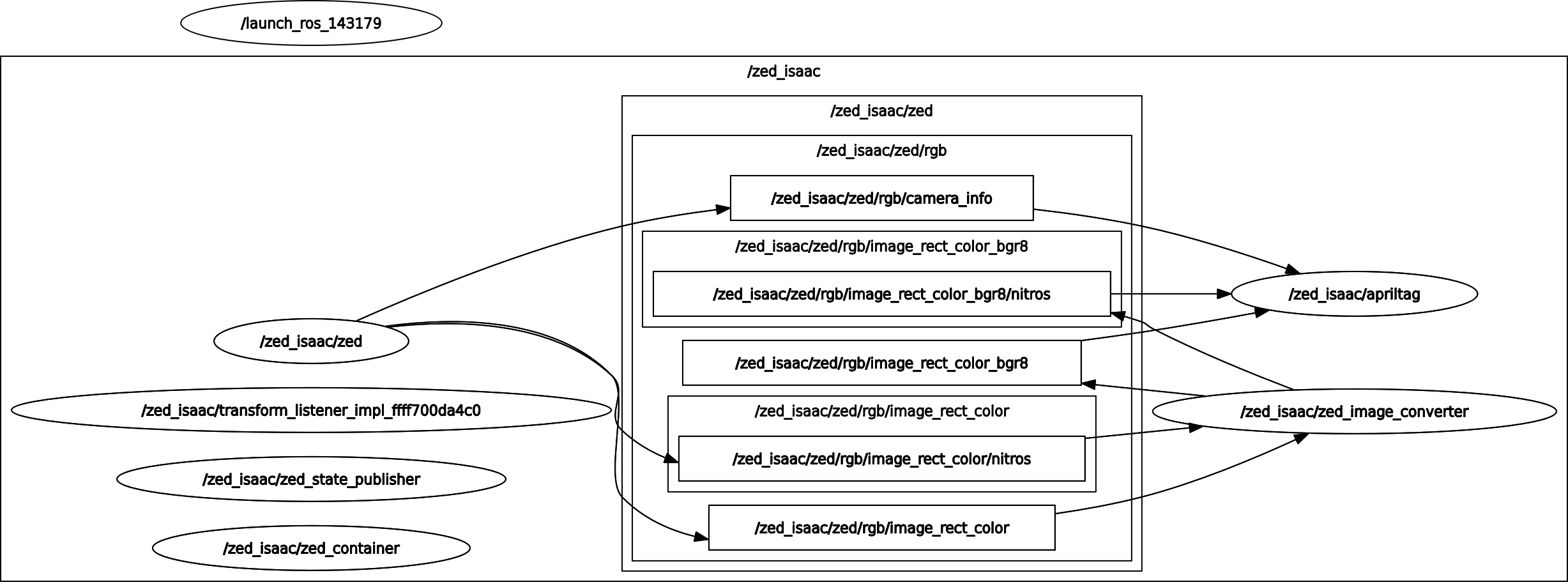
You can visualize the full ROS2 topic graph with:
ros2 run rqt_graph rqt_graph
The launch file explained #
The launch file launch/zed_isaac_ros_april_tag.launch.py is responsible for starting all the necessary nodes and configurations for the AprilTag detection application. It sets up the parameters, including the ZED camera settings and the AprilTag detection parameters, and launches the required nodes in a ROS 2 component container.
Retrieve the configuration parameters from the relative path config/zed_isaac_ros_april_tag.yaml and config/zed_params.yaml:
# Get the path to the camera configuration file
camera_config_override_path = os.path.join(
get_package_share_directory('zed_isaac_ros_april_tag'),
'config',
'zed_params.yaml'
)
# Get the path to the AprilTag configuration file
apriltag_config_path = os.path.join(
get_package_share_directory('zed_isaac_ros_april_tag'),
'config',
'zed_isaac_ros_april_tag.yaml'
)
Create a ROS 2 component container:
# ROS 2 Component Container
container_name = 'zed_container'
info = '* Starting Composable node container: ' + namespace_val + '/' + container_name
actions.append(LogInfo(msg=TextSubstitution(text=info)))
# Note: It is crucial that the 'executable' field is set to be 'component_container_mt'
# so that the created nodes can be started and communicated correctly within the same process.
zed_container = ComposableNodeContainer(
name=container_name,
namespace=namespace_val,
package='rclcpp_components',
executable='component_container_mt',
arguments=['--ros-args', '--log-level', 'info'],
output='screen',
)
actions.append(zed_container)
Create a ZED Component and automatically load it into the container_name container previously created:
# ZED Wrapper launch file
zed_wrapper_launch = IncludeLaunchDescription(
launch_description_source=PythonLaunchDescriptionSource([
get_package_share_directory('zed_wrapper'),
'/launch/zed_camera.launch.py'
]),
launch_arguments={
'camera_model': camera_model,
'container_name': container_name,
'namespace': namespace_val,
'enable_ipc': 'false',
'ros_params_override_path': camera_config_override_path
}.items()
)
actions.append(zed_wrapper_launch)
Setup the Image Format converter resolution by retrieving the information from the camera configuration:
# Read the resolution from the ZED parameters file
with open(camera_config_override_path, 'r') as f:
configuration = yaml.safe_load(f)
print(f'Loaded configuration: {configuration}')
resolution = configuration["/**"]["ros__parameters"]["general"]["grab_resolution"]
pub_resolution = configuration["/**"]["ros__parameters"]["general"]["pub_resolution"]
pub_downscale_factor = configuration["/**"]["ros__parameters"]["general"]["pub_downscale_factor"]
if pub_resolution == 'CUSTOM':
rescale = pub_downscale_factor
else:
rescale = 1.0
if resolution == 'HD2K':
image_width = 2208
image_height = 1242
elif resolution == 'HD1200':
image_width = 1280
image_height = 720
elif resolution == 'HD1080':
image_width = 1920
image_height = 1080
elif resolution == 'HD720':
image_width = 1280
image_height = 720
elif resolution == 'SVGA':
image_width = 960
image_height = 600
elif resolution == 'VGA':
image_width = 672
image_height = 376
Create the Image Format Converter component and set the resolution parameter and the required topic name remappings:
# Isaac ROS Node to convert from ZED BGRA8 image to BGR8 required by AprilTag
isaac_converter_node = ComposableNode(
package='isaac_ros_image_proc',
plugin='nvidia::isaac_ros::image_proc::ImageFormatConverterNode',
name='zed_image_converter',
namespace=namespace_val,
parameters=[
{
'image_width': int(image_width / rescale),
'image_height': int(image_height / rescale),
'encoding_desired': 'bgr8',
'num_blocks': 40
}
],
remappings=[
('image_raw', 'zed/rgb/color/rect/image'),
('image', 'zed/rgb/color/rect/image_bgr8')
]
)
Create the AprilTag component with the required topic name remappings:
# AprilTag detection node
isac_apriltag_node = ComposableNode(
package='isaac_ros_apriltag',
plugin='nvidia::isaac_ros::apriltag::AprilTagNode',
name='apriltag',
namespace=namespace_val,
remappings=[
('image', 'zed/rgb/color/rect/image_bgr8'),
('camera_info', 'zed/rgb/camera_info')
],
parameters=[apriltag_config_path]
)
Load the Image Converter and AprilTag components into the container:
container_full_name = namespace_val + '/' + container_name
# Load the Converter node into the container
load_converter_node = LoadComposableNodes(
composable_node_descriptions=[isaac_converter_node],
target_container=container_full_name
)
actions.append(load_converter_node)
# Load the AprilTag node into the container
load_april_tag_node = LoadComposableNodes(
composable_node_descriptions=[isac_apriltag_node],
target_container=container_full_name
)
actions.append(load_april_tag_node)
The launch file accepts two arguments:
camera_model: The model of the camera being used (e.g., ZED 2i, ZED 2, etc.).disable_tf: IfTruedisable TF broadcasting for all the cameras in order to fuse visual odometry information externally.
These arguments can be passed when launching the file to customize the behavior of the nodes.
Fix the TF issue (optional) #
If you notice that the TF of the detected AprilTags is not correctly propagated, you must download the patched version of the isaac_ros_apriltag package and build it from the source.
Clone the repository into your workspace:
cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}/src
git clone git clone https://github.com/NVIDIA-ISAAC-ROS/isaac_ros_apriltag.git
Fetch the specific Pull Request that contains the fix:
cd isaac_ros_apriltag
git fetch origin pull/64/head:fix_tf
git checkout fix_tf
Build the package:
cd ${ISAAC_ROS_WS}
colcon build --symlink-install --packages-up-to isaac_ros_apriltag
Now you can run the launch file again, and the TF of the detected AprilTags should be correctly propagated.
